Nearly 60% of businesses report stockouts or overstocks due to poor demand visibility. That gap costs time, cash and customer trust across Indian supply chains, and this can be tackled by optimising SAP B1 forecasting
This guide shows how integrated tools in SAP Business One turn raw data into timely insight. Use real-time analytics, visual dashboards and cloud access to align sales, inventory and finance.
Practical methods—from moving averages to predictive analytics and scenario planning—help teams plan purchases, staffing and budgets with confidence. Collaborative demand planning reduces working capital strain and speeds responses to market trends.
We also explain how forecasts link into MRP to trigger replenishment and how advanced techniques capture seasonality and external factors. Readers will find a clear path from data preparation to intelligent forecasting on HANA and extensions to SAP IBP and S/4HANA.
Who benefits? Business leaders, demand planners, supply chain managers and finance controllers seek measurable outcomes: better service levels, lower carrying costs and improved cash flow.
Key Takeaways
- Integrated forecasting improves visibility across sales, inventory and finance.
- Dashboards and analytics convert information into actionable insight for managers.
- Statistical and predictive tools support budgets, purchasing and capacity planning.
- Cloud access enables distributed teams in India to collaborate on up-to-date forecasts.
- Linking forecasts to MRP turns demand signals into timely replenishment actions.
Why accurate SAP B1 forecasting matters today
Better demand visibility turns historical sales and real‑time signals into confident purchasing. Precise demand forecasting helps teams align procurement, production and logistics with actual market needs.

Improved forecast accuracy protects margins by avoiding emergency shipments and reducing excess safety stock. That lowers carrying costs and prevents obsolescence that can drain cash.
Real‑time analytics and clean data let planners spot sudden trends and respond quickly. Continuous measurement of forecast error helps track performance and refine models over time.
- External factors — economic indicators, promotions, competitor moves and weather — shape demand curves and must be monitored.
- Cross‑functional collaboration between sales, marketing and operations validates assumptions to predict future demand.
- Reliable demand forecasting reduces firefighting and enables strategic planning across the supply chain.
- Advanced forecasting techniques increase resilience in volatile markets and fragmented retail channels in India.
When data, analysis and stakeholder buy‑in work together, businesses see better service levels, lower costs and stronger profit performance.
Prepare your data foundation for reliable forecasts
Start by building a single, governed data model that brings sales, POS and logistics into one view. Centralised data reduces conflicting numbers and creates a trusted baseline for analysis.
Consolidate historical sales data, point‑of‑sale feeds, seasonality and supply chain metrics into one repository. Include key attributes: item codes, warehouse locations, lead times, service levels, calendar hierarchies and promotion flags.
Cleanse records to deduplicate customers and items, standardise units and harmonise calendars. Use based historical data transformations to align weekly and monthly periods before model training.
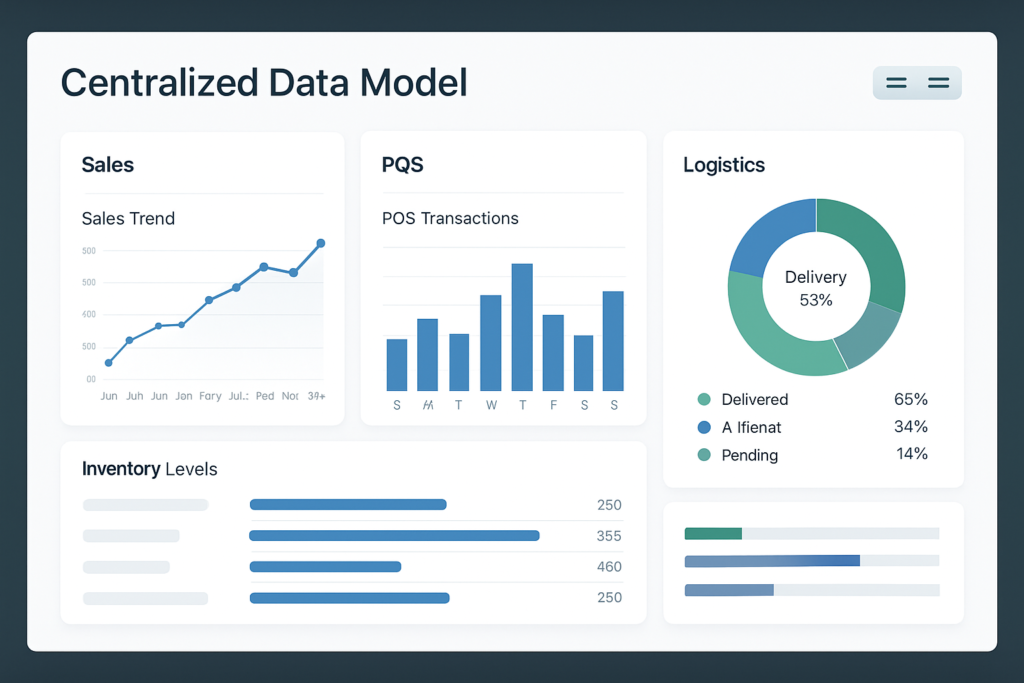
Enrich datasets with external trends such as CPI, festival calendars, monsoon impact and competitor activity. Run validation routines: gap checks, outlier detection and reconciliation with financials to ensure trusted information.
- Define role‑based access so planners, finance and sales see the right dashboards without manual extracts.
- Build interactive dashboards in SAP Business One to monitor sell‑in, sell‑out and channel performance in real time.
- Capture metadata and lineage to sustain auditability and speed change management across business units.
How to use Intelligent Forecasting in SAP Business One on HANA
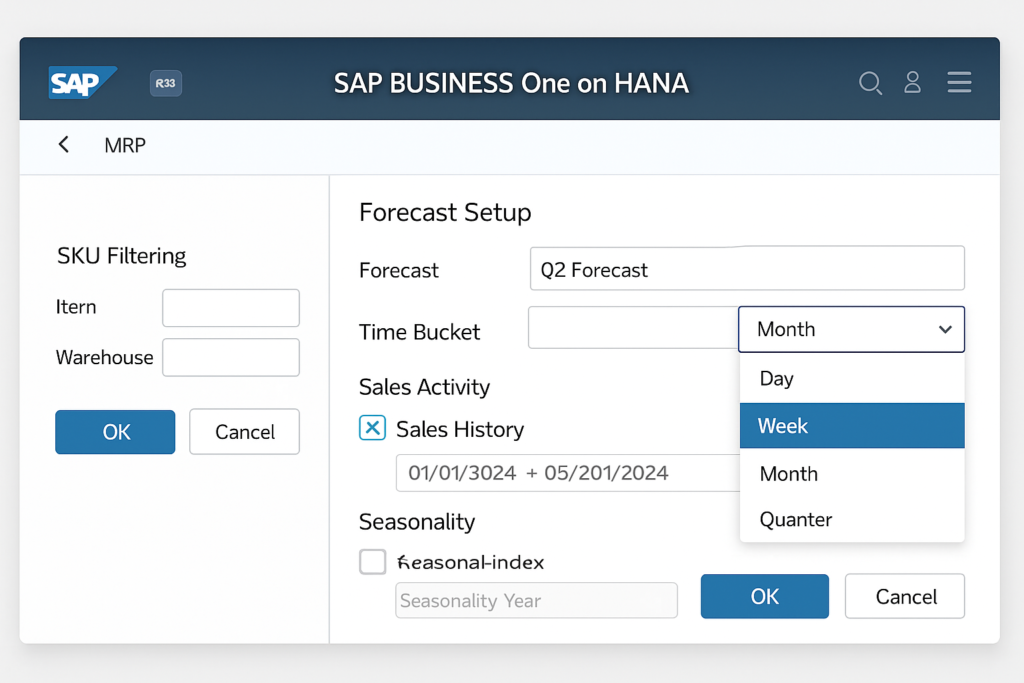
Start from Modules > MRP > Forecasts to build forecasts that reflect real sales activity and seasonality.
Choose daily, weekly or monthly time buckets and set the planning horizon before you select items and warehouses
Filter and page through large catalogues to include only relevant SKUs. Pick the sales history source—Sales Orders, Deliveries or A/R Invoices—because each source changes the signal quality and future estimates.
- Automatic model selection on HANA applies TESM and LRDTSA as advanced forecasting models for trend and regression analysis.
- SQL Server editions fall back to manual or flat average methods, so HANA gives better real‑time models and analysis.
- Use the visual chart to confirm level, trends and seasonality, then adjust outliers to avoid skewing results while keeping an audit trail.
- Run multiple scenarios, compare results, save templates and push the approved forecast into the MRP Wizard to generate material and procurement plans.
Document assumptions, parameters and chosen models so teams in India can repeat runs and govern outcomes. This ensures data integrity and quicker decision cycles using the business one toolset.
Extend forecasting with SAP IBP and SAP S/4HANA
Bring time‑series engines and machine learning into one planning layer to deliver precise, actionable forecasts. Use enterprise algorithms and live market feeds together so teams can react faster to demand shifts.
SAP IBP acts as the analytical layer for time‑series, ARIMA, regression, decision trees and machine learning algorithms at enterprise scale. Configure model classes to match product categories and lifecycles so models fit SKU‑location behaviour.
Leverage time-series, regression and machine learning models for precision
Apply advanced forecasting and predictive analytics to detect demand shifts early. Model selection and parameter tuning at the SKU level improves accuracy and reduces safety stock.
Incorporate real-time market signals and enable collaborative scenario planning
SAP S/4HANA ingests POS, competitor pricing and sentiment data to predict future demand and automate replenishment rules. Shared dashboards provide a single source of truth via integrated business planning.
- Match IBP model classes to lifecycles for better precision.
- Run collaborative scenarios that align merchandising, supply and finance.
- Push approved outputs back to SAP business systems for execution and fulfilment.
Improve forecast accuracy and inventory performance
Measure and refine your models continuously to tighten error bands and raise inventory service levels. Use clear KPIs, post-event review and automation so teams act on insight rather than intuition.
Track forecast accuracy metrics and post-event analysis
Define KPIs such as MAPE, bias and MAD and set thresholds by product segment. Run post-event analysis to quantify the impact of promotions, festivals and supply shocks on actual versus planned.
Link demand forecasts to replenishment to reduce carrying costs
Push approved forecasts into replenishment rules so purchase and transfer orders trigger at the right time and quantity. Integrate lead-time variability and minimum order quantities to stabilise fulfilment and reduce carrying costs.
Adopt predictive analytics for continuous model refinement
- Define accuracy KPIs (MAPE, bias, MAD) and thresholds for lifecycle segments.
- Conduct post-event analysis to measure promotion and holiday effects on sales.
- Link forecasts to replenishment rules so orders auto-trigger to match demand.
- Use inventory health dashboards to balance service levels, obsolescence and working capital.
- Apply AI-driven analytics to learn from error patterns and update models automatically.
- Segment portfolios (A/B/C, new vs mature) and assign model and safety-stock policies.
- Factor supplier lead-time variability and MOQs into planning to stabilise supply.
- Share forecast and inventory insights with sales and finance to align targets and cash flow.
Practical outcome: Continuous analytics and linked replenishment lower excess inventory, improve performance and help Indian businesses reduce carrying costs while keeping service high.
SAP B1 forecasting: steps to act now
Turn forecasting outputs into actions by mapping them to inventory, procurement and finance calendars. That link ensures plans move from analysis into execution and protects service levels.
Align forecasts with business objectives and demand planning processes
Define planning horizons, ownership and approval workflows that match your strategic goals. Standardise a demand planning calendar with S&OP checkpoints and clear cutoff dates.
Document model choices and service‑level targets for each segment so decisions remain consistent. Start with priority categories and expand as data quality and process maturity improve.
Deploy cloud accessibility for teams and scale capabilities as you grow
Enable cloud access so regional and field teams can collaborate on a single, current plan without manual files. Cloud tools offer real‑time updates and scalable compute as volumes rise.
- Establish a cadence for accuracy tracking, root‑cause analysis and parameter tuning — an ongoing process requires discipline.
- Integrate forecasts with procurement, production and finance calendars to ensure execution readiness.
- Build a skills roadmap for planners on tools, statistics and storytelling to predict future demand credibly.
Conclusion
A robust data strategy turns scattered sales records and market signals into reliable plans for action.
Clean historical data, tested models and real‑time analytics together enhance forecasting accuracy across the supply chain. Use SAP Business One on HANA for trend and seasonality detection, with outlier control to protect predictions.
Extend to sap s/4hana and integrated business planning to scale models, machine learning and predictive analytics for enterprise execution. Track KPIs, run post‑event reviews and refine parameters regularly.
Start with priority SKUs, validate predictions in short cycles, then standardise what works. The result: better service levels, lower carrying costs and faster responses to market change in India.
Formalise ownership, align processes and invest in data and skills to realise measurable outcomes from forecasts.

